Unlocking the Future of Manufacturing with Rapid 3D Prototyping
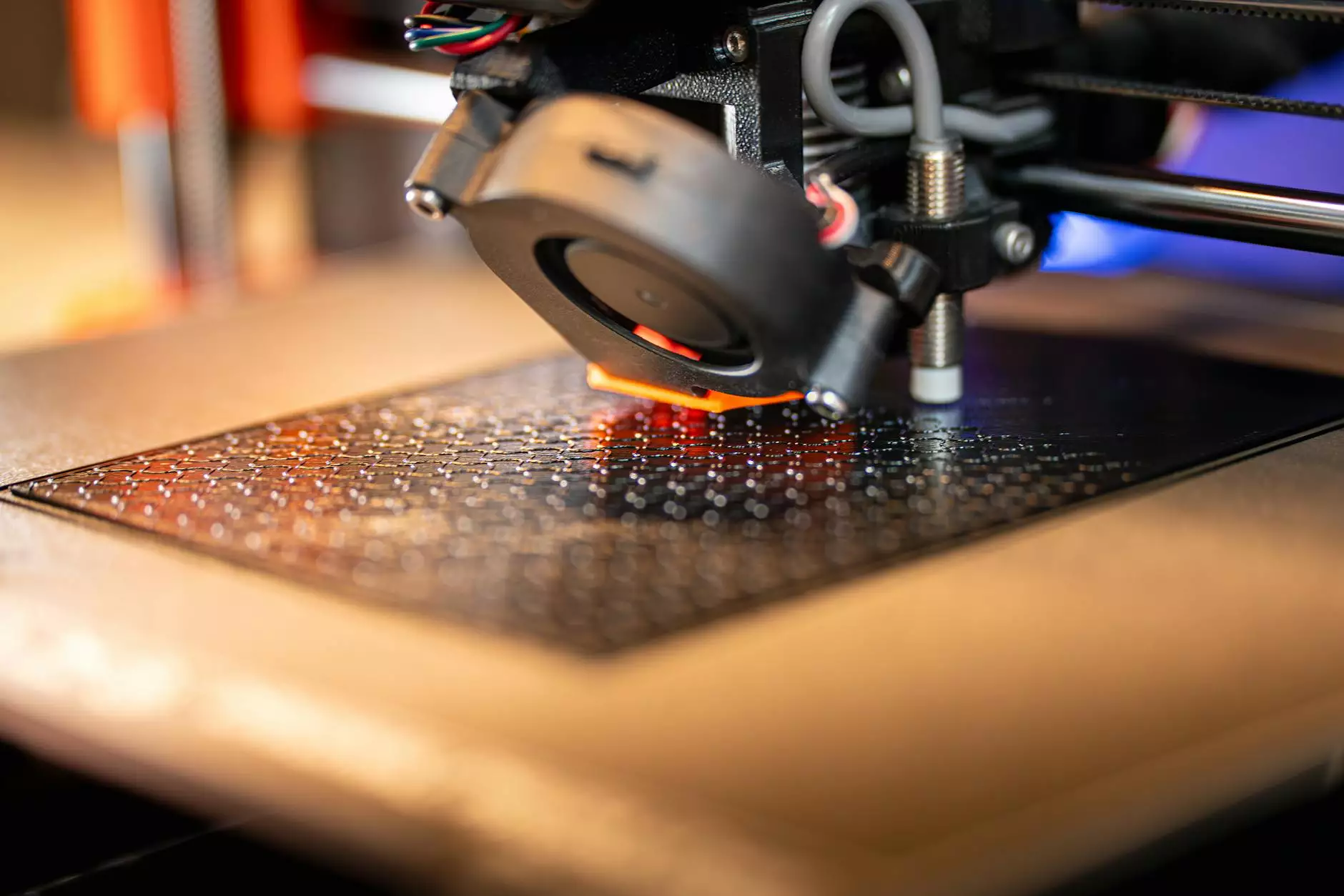
As the landscape of manufacturing continues to evolve, rapid 3D prototyping has emerged as a groundbreaking solution that is reshaping the way metal fabricators operate. This innovative technology allows for the swift creation of prototype models, enabling businesses to bring their ideas to fruition faster and more efficiently than ever before.
What is Rapid 3D Prototyping?
Rapid 3D prototyping refers to a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using 3D computer-aided design (CAD) data. This manufacturing process is particularly vital in fields that rely on metal fabrication, as it enables designers and engineers to create and test their products before committing to mass production.
Advantages of Rapid 3D Prototyping
The application of rapid 3D prototyping in metal fabrication offers a multitude of advantages:
- Reduced Time to Market: By allowing for quicker iterations, businesses can significantly reduce their time to market, responding faster to customer needs and industry trends.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional prototyping methods can be expensive and labor-intensive. Rapid prototyping minimizes these costs by streamlining the production process.
- Enhanced Customization: With the ability to rapidly prototype, businesses can easily create customized designs that meet specific client requirements, offering a competitive edge.
- Improved Design Quality: Rapid prototyping enables designers to visualize their concepts, providing opportunities for critical feedback and iterative improvements, ultimately leading to better products.
- Lower Risk of Production Errors: Early prototypes help identify design flaws before moving to full-scale production, thereby reducing costly errors.
The Process of Rapid 3D Prototyping
The process of rapid 3D prototyping involves several key steps:
- Step 1: Design Creation - Using CAD software, designers create a detailed model of the product.
- Step 2: File Preparation - The CAD file is converted into a format suitable for the 3D printer, typically STL.
- Step 3: Prototyping - A 3D printer or other advanced manufacturing equipment then constructs the prototype layer by layer.
- Step 4: Post-Processing - This step may involve smoothing surfaces, painting, or any necessary adjustments to enhance the final prototype.
- Step 5: Testing & Feedback - The prototype undergoes evaluations to ensure it meets design specifications and performance standards.
The Technologies Behind Rapid 3D Prototyping
Several technologies contribute to the realm of rapid 3D prototyping, each serving unique purposes within the fabrication process. Some notable methods include:
- Stereolithography (SLA): Utilizes lasers to cure liquid resin into solid objects, known for producing high-detail prototypes.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Involves melting thermoplastic filaments to create solid models, favored for its cost-effectiveness.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Employs a laser to fuse powdered materials, widely used for creating durable prototypes from a variety of materials, including metals.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA but uses a digital light projector to cure resin, enabling rapid and precise layering.
- Binder Jetting: A method that uses a binder to join powder materials, allowing for detailed pieces and multi-material prototypes.
The Role of Metal Fabricators in 3D Prototyping
Metal fabricators play a crucial role in the rapid 3D prototyping landscape by integrating advanced technologies to enhance manufacturing capabilities. At DeepMould.net, we utilize state-of-the-art equipment and expertise in metal fabrication to produce top-quality prototypes that meet stringent industry standards.
We focus on:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right material is paramount, as it impacts performance, aesthetics, and manufacturing processes.
- Process Optimization: Continuous improvement of our techniques ensures that we remain at the forefront of the rapid prototyping industry.
- Collaboration: Working closely with clients allows for a deeper understanding of their needs, resulting in tailored solutions that enhance product development.
Transforming Ideas into Reality
The primary goal of rapid 3D prototyping is to swiftly turn ideas into tangible products. Metal fabricators enhance this capability by providing a seamless link between design and production. As a result, businesses can test concepts, gather feedback, and make necessary adjustments, all before investing heavily in mass manufacturing.
Future Trends in Rapid 3D Prototyping and Metal Fabrication
Looking ahead, the landscape of rapid 3D prototyping and metal fabrication is expected to evolve further. Here are some emerging trends:
- Increased Adoption of AI: Artificial intelligence will enhance design processes and manufacturing efficiencies, enabling smarter production capabilities.
- Materials Innovation: Ongoing research will lead to the development of advanced materials, improving durability and functionality for various applications.
- Integration with IoT: The Internet of Things will provide real-time data analytics, allowing for better monitoring and control of fabrication processes.
- Sustainability Practices: A growing emphasis on eco-friendly manufacturing processes will drive innovations in materials and resource management.
- Customization at Scale: Advances will allow manufacturers to offer personalized products without sacrificing efficiency, transforming customer experiences.
Conclusion: Embracing Innovation in Metal Fabrication
In conclusion, rapid 3D prototyping has revolutionized the way metal fabricators operate, enabling quicker, more efficient, and cost-effective manufacturing solutions. As businesses increasingly recognize the benefits of this technology, those who adapt and innovate will thrive in the competitive landscape.
At DeepMould.net, we are committed to harnessing the power of rapid 3D prototyping to help businesses streamline their operations, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Embracing these advancements positions us—and our clients—for success in the future of manufacturing.